Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hata, Koji*; Niunoya, Sumio*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Miyara, Nobukatsu*
Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 16(2), p.365 - 378, 2024/02
Excavation of underground caverns, such as mountain tunnels and energy-storage caverns, may cause the damages to the surrounding rock as a result of the stress redistribution. In this influenced zone, new cracks and discontinuities are created or propagate in the rock mass. Therefore, it is effective to measure and evaluate the acoustic emission (AE) events generated by the rocks, which is a small elastic vibration, and permeability change. The authors have developed a long-term measurement device that incorporates an optical AE (O-AE) sensor, an optical pore pressure sensor, and an optical temperature sensor in a single multi-optical measurement probe (MOP). Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D activities to enhance the reliability of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) deep geological disposal technology. In a high-level radioactive disposal project, one of the challenges is the development of methods for long-term monitoring of rock mass behavior. Therefore, in January 2014, the long-term measurements of the hydro-mechanical behavior of the rock mass were launched using the developed MOP in the vicinity of 350 m below the surface at the Horonobe Underground Research Center. The measurement results show that AEs occur frequently up to 1.5 m from the wall during excavation. In addition, hydraulic conductivity increased by 2 to 4 orders of magnitude. Elastoplastic analysis revealed that the hydraulic behavior of the rock mass affected the pore pressure fluctuations and caused micro-fractures. Based on this, a conceptual model is developed to represent the excavation damaged zone (EDZ), which contributes to the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste.
Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Materials, 16(17), p.5830_1 - 5830_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Cavitation damage on the mercury target vessel is induced by proton beam injection in mercury. The prediction method of the cavitation damage using Monte Carlo simulations was proposed taking into account of the uncertainties of the position of cavitation bubbles and impact pressure distributions. The distribution of impact pressure attributed to individual cavitation bubble collapsing was assumed to be the Gaussian distribution, and the probability distribution of the maximum value of impact pressures was assumed to be three kinds of distributions; the delta function, the Gaussian and Weibull distributions. Two parameters were estimated using Bayesian optimization by comparing the distribution of the cavitation damage obtained from experiment with that of accumulated plastic strain obtained from the simulation. It was found that the results obtained using the Weibull distribution reproduced the actual cavitation erosion phenomenon better than the other results.
Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Tanabe, Makoto*
Jikken Rikigaku, 23(2), p.168 - 174, 2023/06
Cavitation damage on the inner surface of the mercury target for the spallation neutron source occurs by proton bombarding in mercury. The prediction method of the cavitation damage using Monte Carlo simulations was suggested taking variability of the bubble core position and impact pressure distribution into account. The impact pressure distribution was estimated using the inverse analysis with Bayesian optimization was conducted with comparison between cavitation damage distribution obtained from experiment and the cumulative plastic strain distribution obtained from simulation. The average value and spread of maximum impact pressure estimated assuming the Gaussian distribution were 3.1 GPa and 1.2  m, respectively. Simulation results reproduced experimental results and it can be said that this evaluation method is useful.
m, respectively. Simulation results reproduced experimental results and it can be said that this evaluation method is useful.
 C
CMiyazawa, Takeshi; Kikuchi, Yuta*; Ando, Masami*; Yu, J.-H.*; Yabuuchi, Kiyohiro*; Nozawa, Takashi*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu*; Nogami, Shuhei*; Hasegawa, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 575, p.154239_1 - 154239_11, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Konno, Chikara
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 6 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced in 2017 and those of 22 nuclei for neutron and 25 nuclei for proton were bundled in the PHITS code. Recently it was found that the following five data in the JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files had any problems; ACE files for  N and
N and  O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
O, heating numbers, damage energy production cross sections, secondary neutron multiplicities and fission cross sections. Thus new JENDL-4.0/HE neutron and proton ACE files were produced with the problems fixed. This paper describes the problems and how to produce the new neutron and proton ACE files in detail.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*; Naoe, Shota*; Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 63(5), p.719 - 729, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.19(Biology)Naoe, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-018, 43 Pages, 2022/08
In the liquid mercury target system for the pulsed spallation neutron source of Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), cavitation that is generated by the high-energy proton beam-induced pressure waves, resulting severe erosion damage on the interior surface of the mercury target vessel. The erosion damage is increased with increasing the proton beam power, and has the possibility to cause the leakage of mercury by the penetrated damage and/or the fatigue failure originated from erosion pits during operation. To achieve the long term stable operation under high-power proton beam, the mitigation technologies for cavitation erosion consisting of surface modification on the vessel interior surface, helium gas microbubble injection, double-walled beam window structure has been applied. The damage on interior surface of the vessel is never observed during the beam operation. Therefore, after the target operation term ends, we have cut out specimen from the target nose of the target vessel to inspect damaged surface in detail for verification of the cavitation damage mitigation technologies and lifetime estimation. We have developed the techniques of specimen cutting out by remote handling under high-radiation environment. Cutting method was gradually updated based on experience in actual cutting for the used target vessel. In this report, techniques of specimen cutting out for the beam entrance portion of the target vessel in high-radiation environment and overview of the results of specimen cutting from actual target vessels are described.
Oka, Hiroshi; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Tachi, Yoshiaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 547, p.152833_1 - 152833_7, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to evaluate the stability of nano-sized oxide particles and matrix structure of ODS cladding tube, which are the determinants of their high temperature strength, the microstructural observation was carried out after internal pressurized creep test at 700 C for over 45,000 hours. The specimens were the as-received and crept specimens of 9Cr-ODS steel with tempered martensite and 12Cr-ODS steel with recrystallized ferrite. Small platelet was cut out from the crept pressurized tube, then thinned to foil. Microstructural observation was conducted with TEM JEOL 2010F. As a result of the observation, it was confirmed that the size and number density of the nano-sized particles were almost unchanged even after the creep test. In addition, the tempered martensite structure, which is one of the determinants of the creep strength of 9Cr-ODS steel, was not significantly different between the as-received and crept specimen, indicating the stability of their matrix structure.
C for over 45,000 hours. The specimens were the as-received and crept specimens of 9Cr-ODS steel with tempered martensite and 12Cr-ODS steel with recrystallized ferrite. Small platelet was cut out from the crept pressurized tube, then thinned to foil. Microstructural observation was conducted with TEM JEOL 2010F. As a result of the observation, it was confirmed that the size and number density of the nano-sized particles were almost unchanged even after the creep test. In addition, the tempered martensite structure, which is one of the determinants of the creep strength of 9Cr-ODS steel, was not significantly different between the as-received and crept specimen, indicating the stability of their matrix structure.
Oka, Hiroshi*; Kaito, Takeji; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Otsuka, Satoshi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 370, p.110894_1 - 110894_8, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The objective of this study is to evaluate the reliability of a cumulative damage fraction (CDF) analysis for the prediction of fuel pin breach in fast rector using experimentally obtained fuel pin breach data for the first time. Six breached fuel pins were obtained from steady state irradiation in the EBR-II. Post irradiation examinations revealed that FP gas pressure was the main cause of creep damage in cladding, and that the stress contribution from FCMI was negligible. CDFs evaluated for these pins using in-reactor creep rupture equation, taking into account the irradiation history of cladding temperature and hoop stress due to FP gas pressure, were in the range of 0.7 to 1.4 at the occurrence of breach. This shows clearly that fuel pin breach occurs when the CDF approaches 1.0. The results indicate that CDF analysis would be a reliable method for the prediction of fuel pin breach when appropriate material strength and environmental effects are adopted.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(10), p.1141 - 1151, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)To estimate the structural damages of materials in accelerator facilities, displacement per atom (dpa) is widely employed as a damage index, calculated based on the displacement cross-section obtained using a calculation model. Although dpa is applied as standard, the experimental data of the displacement cross-section for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV are scarce. Among the calculation models, difference of about factor 8 exist, so that the experimental data of the cross-section are crucial to validate the model. To obtain the displacement cross-section, we conducted experiments at J-PARC. The displacement cross-section of copper and iron was successfully obtained for a proton projectile with the kinetic energies, 0.4 - 3 GeV. The results were compared with those obtained using the widely utilized Norgertt-Robinson-Torrens (NRT) model and the athermal-recombination-corrected (arc) model based on molecular dynamics. It was found that the NRT model overestimates the present displacement cross-section by 3.5 times. The calculation results obtained using with the arc model based on the Nordlund parameter show remarkable agreement with the experimental data. It can be concluded that the arc model must be employed for the dpa calculation for the damage estimation of copper and iron.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Chen, Y.*; Ishii, Eiichi; Sakurai, Akitaka; Miyara, Nobukatsu; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2019-011, 50 Pages, 2020/03
In this research, we performed the resin injection experiment at the 350 m Gallery of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory in order to identify the distribution of fractures induced around the gallery owing to excavation. We also observed the rock cores obtained around the resin injection borehole under ultraviolet light. As a result, the extent of the development of EDZ fracture was 0.9 m from the gallery wall. In the depth within 0.4 m from the gallery wall, the density of the EDZ fracture is higher than the depth more than 0.4 m from the gallery wall. As a result of the analysis on the fracture aperture by image processing, the fractures with a large aperture (1.02 mm in maximum) were observed within 0.3 m from the gallery wall, while the maximum aperture was 0.19 mm in the depth more than 0.3 m from the gallery wall.
Takada, Hiroshi; Haga, Katsuhiro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.081003_1 - 081003_7, 2020/02
At the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), the pulsed spallation neutron source has been in operation with a redesigned mercury target vessel from October 2017 to July 2018, during which the operational beam power was restored to 500 kW and the operation with a 1-MW equivalent beam was demonstrated for one hour. The target vessel includes a gas-micro-bubbles injector and a 2-mm-wide narrow mercury flow channel at the front end as measures to suppress the cavitation damage. After the operating period, it was observed that the cavitation damage at the 3-mm-thick front end of the target vessel could be suppressed less than 17.5  m.
m.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Chen, Y.*; Ishii, Eiichi; Sakurai, Akitaka; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*
Proceedings of 5th ISRM Young Scholars' Symposium on Rock Mechanics and International Symposium on Rock Engineering for Innovative Future (YSRM 2019 and REIF 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/12
In the excavation of a repository for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal, it is important to understand the hydro-mechanical characteristics of the Excavation Damaged Zone (EDZ) induced around the gallery because EDZ can lead to the migration pathway of radionuclides. Thus, we performed the resin injection experiment at the 350 m gallery of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory in Japan to investigate the characteristics of fractures induced around the gallery wall in excavation. In the experiment, we developed a low viscosity resin mixed with a fluorescent substance and injected to the borehole drilled about 1 m in length. After the experiment, we overcored around the injection borehole. The observation on the cut surface of the overcore under ultraviolet light revealed that the fractures were distributed within 0.8 m from the gallery wall. Fractures are interconnected each other in particular within 0.25 m from the niche wall. Furthermore, fractures with large aperture (about 1.0 mm) were developed in that region. These observed results will be fundamental information for understanding of the fracturing process in the EDZ.
Tsai, P.-E.; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 121(1), p.13 - 16, 2019/11
The importance of PKA characteristics to radiation damage assessment for proton accelerators has been demonstrated in the paper by the PHITS simulations. In order to obtain accurate results of displacement cross section calculated by PHITS, it is therefore critical to have the physics models implemented in PHITS be properly validated by experimental data. With the new measurement system, which has been being developed here at JAEA, it is expected to provide experimental PKA data with low measurement thresholds and good mass resolutions. The test result we obtained at CYRIC, Tohoku University, for the 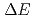 -
- gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
gas ionization chamber as a part of the new measurement system was very promising. We were able to successfully distinguish C, B, Be, Li, and He elements with threshold energies lower than 1 MeV/nucleon in the configuration of 70-MeV proton beam and 920-nm thick C target. More experiments and tests shall continue in the future with heavier targets and higher proton beam energies.
Okumura, Taiga*; Yamaguchi, Noriko*; Dohi, Terumi; Iijima, Kazuki; Kogure, Toshihiro*
Microscopy, 68(3), p.234 - 242, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.41(Microscopy)Radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), consisting substantially of silicate glass, were released to the environment during the Fukushima nuclear accident in March 2011. We investigated a total of nine CsMPs using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and inferred the atmosphere in the reactors during the accident. From elemental mapping using energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry, Fe and Zn showing radial inhomogeneities were found in the CsMPs, in addition to the Cs that had been previously reported. Four of the CsMPs included submicron crystals, which were identified as chromite, franklinite, acanthite, molybdenite, and hessite. The chromium-containing spinels, chromite and franklinite, indicated the presence of ferrous iron (Fe ), suggesting that the inside of the reactors was reductive to some extent. Electron energy-loss spectroscopy also confirmed that the CsMPs did not contain boron, and therefore the atmosphere in which they were formed might be boron-free.
), suggesting that the inside of the reactors was reductive to some extent. Electron energy-loss spectroscopy also confirmed that the CsMPs did not contain boron, and therefore the atmosphere in which they were formed might be boron-free.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Tokiwa, Tetsuya*; Sato, Toshinori; Hayano, Akira
Proceedings of 2019 Rock Dynamics Summit in Okinawa (USB Flash Drive), p.682 - 687, 2019/05
In high-level radioactive disposal projects, it is important to investigate the extent of the excavation damaged zone (EDZ) for safety assessment because EDZ can provide a migration pathway for radionuclides from the facility. To investigate the quantitative differences between EDZs formed because of blasting and mechanical excavation, we studied the characteristics of fractures induced by excavation based on fracture mapping performed during shaft sinking (V- and E-Shafts). As a result, it was found that blasting excavation can lead to the formation of a large number of newly created fractures (EDZ fractures) compared with mechanical excavation. In addition, the seismic velocity (P-wave velocity) measured during blasting excavation (E-Shaft) was lower than that measured during mechanical excavation (V-Shaft). Furthermore, we found that the support pattern that reinforces forward rocks to be appropriate for limiting damage to the shaft wall.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi
Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 52(2), p.385 - 401, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:67.51(Engineering, Geological)Excavation of deep underground openings induces permeable fractures around the opening due to stress redistribution. Such a zone is called excavation damaged zone (EDZ). In a high-level radioactive waste disposal project, the EDZ might provide pathways for the migration of radionuclides around the facility. Thus, this study focused on the development of a method for estimating the highest potential hydraulic conductivity in the EDZ around a gallery in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan. Borehole televiewer surveys, rock core observations, and hydraulic tests were undertaken to investigate the extent and magnitude of hydraulic conductivity in the EDZ around the gallery. The observed extent of the EDZ shows good agreement with the EDZ estimated from hydro-mechanical coupling analysis. The measured hydraulic conductivities of the EDZ are within the range of those based on the Mean Stress Index (MSI), which is defined as the ratio of the effective mean stress derived from numerical analyses to the tensile strength of intact rock. Given that the rock mass is relatively homogeneous and artificial damage (e.g., blasting-induced damage) can be neglected, as in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, the MSI model is likely to be applicable in estimating the highest potential hydraulic conductivity in the EDZ.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Miyara, Nobukatsu; Ishii, Eiichi; Nakayama, Masashi; Kimura, Shun
Proceedings of 13th SEGJ International Symposium (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2018/11
The construction of underground facilities induces fractures in the rock mass around the underground voids due to the resultant stress redistribution. This has particular implications for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal projects, where fracture development creates an excavation damaged zone (EDZ) that increases the hydraulic conductivity of the surrounding rock mass and can provide a pathway for the migration of radionuclides from the storage facilities. It is therefore important to understand the long-term evolution of the EDZ and perform a comprehensive HLW disposal risk assessment. An in situ engineered barrier system experiment was conducted in the 350 m gallery at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, to observe the near-field coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) process in situ and validate coupled THMC models. Here we investigate the evolution of the EDZ around the gallery and model a test pit that was excavated below the floor of the gallery using a series of seismic tomography surveys. There was a significant decrease in the seismic velocity field around the test pit due to its excavation, which became slightly more pronounced over time after the excavation. These seismic results, coupled with hydraulic tests and pore pressure measurements around the pit, indicate that fracture development and the decrease in saturation around the test pit resulted in a decrease in the seismic velocity field after the excavation of the test pit. Furthermore, the increase in saturation around the test pit is a key reason for the increase in the seismic velocity field after the heater test.
Nishino, Hiroyuki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kurisaka, Kenichi
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 5(4), p.18-00079_1 - 18-00079_17, 2018/08
Sugita, Yutaka; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Kubota, Kenji*; Nakata, Eiji*; Oyama, Takahiro*
JAEA-Research 2018-002, 72 Pages, 2018/06
In a excavation of shafts and galleries in the deep underground for disposing radioactive waste, an excavation damaged zone (EDZ) is developed around the galleries and shafts owing to the stress redistribution. Since the characteristic changes of the rock mass in the EDZ affects the radionuclides migration behavior, it is important to understand the long-term behavior of the EDZ. Thus, we performed the in situ experiment to investigate the long-term behavior of EDZ as part of the collaborative research between Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry in the 140m gallery in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. In this research, we investigated the extent, mechanism of the change of hydro-mechanical characteristic, and long-term behavior of the EDZ on the basis of the comprehensive estimation of the results of the observation of the drift wall and the various investigations using boreholes such as geological investigation, the seismic and resistivity tomography, hydraulic test, water content monitoring, borehole loading test, convergence measurement, and so on. In addition, we clarified applicability and future tasks of the testing method used in this research for the investigation of the long-term behavior of the EDZ.